Published 29 October 2024 –
In today’s business landscape, the importance of corporate sustainability cannot be overstated. Businesses across various industries are increasingly integrating sustainability into their core operations, and this growing trend has been accelerated by the rise in mandatory ESG reporting regulations globally. With over 8,000 companies and countries representing 90 percent of global GDP pledging net-zero emissions by 2050, there has been meaningful momentum towards sustainability. Despite this, McKinsey’s scenarios indicate that global emissions are unlikely to reach net-zero by the end of this century without significant changes.
However, with companies still lacking clear success metrics and regulations clamping down on greenwashing practices on the rise, the critical need for a comprehensive Corporate Sustainability roadmap arises.
How can businesses capitalise on this new opportunity? To truly reap the benefits that sustainability offers, companies should incorporate sustainability as an intrinsic part of their business strategy.
What’s the Benefit of Corporate Sustainability?
Incorporating ESG priorities into growth strategies can significantly benefit companies, including tangible financial benefits. A McKinsey study found that financially successful companies that integrated ESG principles were twice as likely as their peers to achieve a 10% increase in revenue.
Moreover, by 2024, nearly 50,000 companies will be required to engage in mandatory sustainability reporting. Companies that get ahead of these regulations by embedding sustainability into their core strategies will be better positioned to meet these requirements and stay competitive.
Managing supply chain sustainability is also another critical aspect to take note of. For instance, companies that manage their supply chain sustainability are better equipped to handle disruptions caused by extreme weather events. These disruptions can be mitigated through proactive sustainability measures, ensuring a more resilient and reliable supply chain.
Lastly, embracing sustainability can boost confidence among investors, customers, and financiers. In today’s market, stakeholders are increasingly looking for companies that not only talk about sustainability but also take concrete actions towards achieving it. This includes employees as well, with a recent IBM survey showing that employees increasingly seek out employers whose values align with their own commitment to sustainability.
Steps to achieve Corporate Sustainability
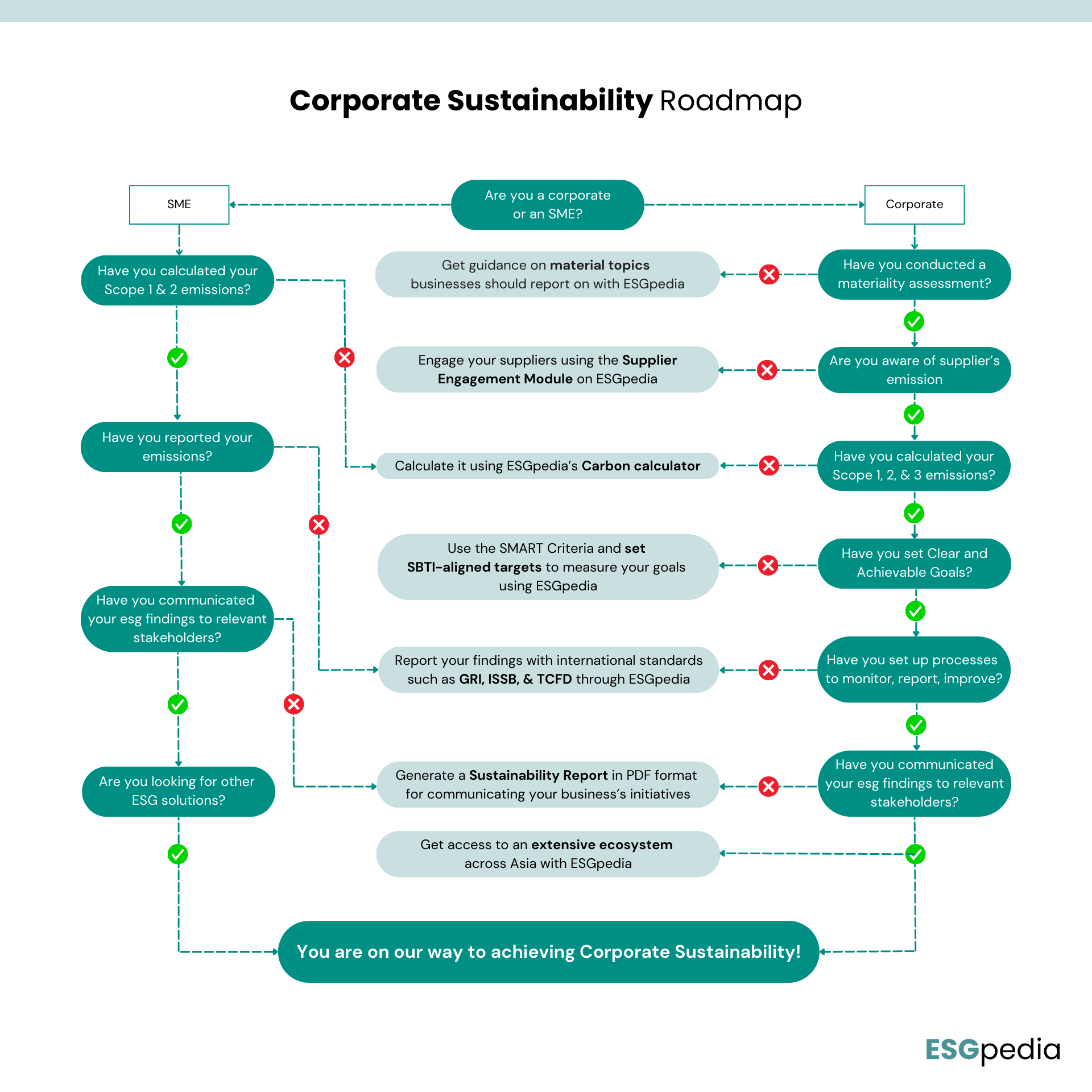
Step 1: Assess Your Current Sustainability Status
Assessing the current sustainability status is a key first step for any corporate entity aiming to develop a robust sustainability strategy. To effectively prioritize sustainability efforts, corporates should conduct a comprehensive Materiality Assessment. This assessment helps identify and prioritize the topics that matter most to both the business and its stakeholders.
A material issue is one that significantly impacts the business in terms of growth, cost, or risk, and is also considered important by the company’s stakeholders. By focusing on these material issues, companies can create real sustainable value. ESGpedia offers guidance on the material topics businesses should report on, enabling them to compute and analyse these critical factors efficiently. Important areas to assess include the company’s carbon footprint, waste management, and energy usage.
What about SMEs?
- For SMEs, assessing the current sustainability status is equally important, although the approach can be more streamlined compared to larger corporates. Given their smaller scale, SMEs may not require extensive materiality assessments. Instead, they can leverage starter tools like those provided by ESGpedia to get a clear understanding of their ESG status without the complexity that larger organizations face. The ESGpedia Starter Tool includes a pre-assessment for ESG requirements, a Scope 1 and 2 GHG Calculator, and access to the ESBN Asia-Pacific Green Deal Program.
Step 2: Calculating the GHG Emissions
Accurately calculating emissions is the next fundamental step in any sustainability plan. Understanding and quantifying emissions helps organisations further identify key areas where they can reduce their carbon footprint, optimize resource use, and enhance overall sustainability performance.
To meet immediate reporting requirements, the focus can be placed on calculating and reporting Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, as a start. Scope 1 emissions are direct greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from sources owned or controlled by the company, such as fuel combustion in company vehicles and manufacturing processes. Scope 2 emissions, on the other hand, are indirect GHG emissions from the consumption of purchased electricity, steam, heating, and cooling.
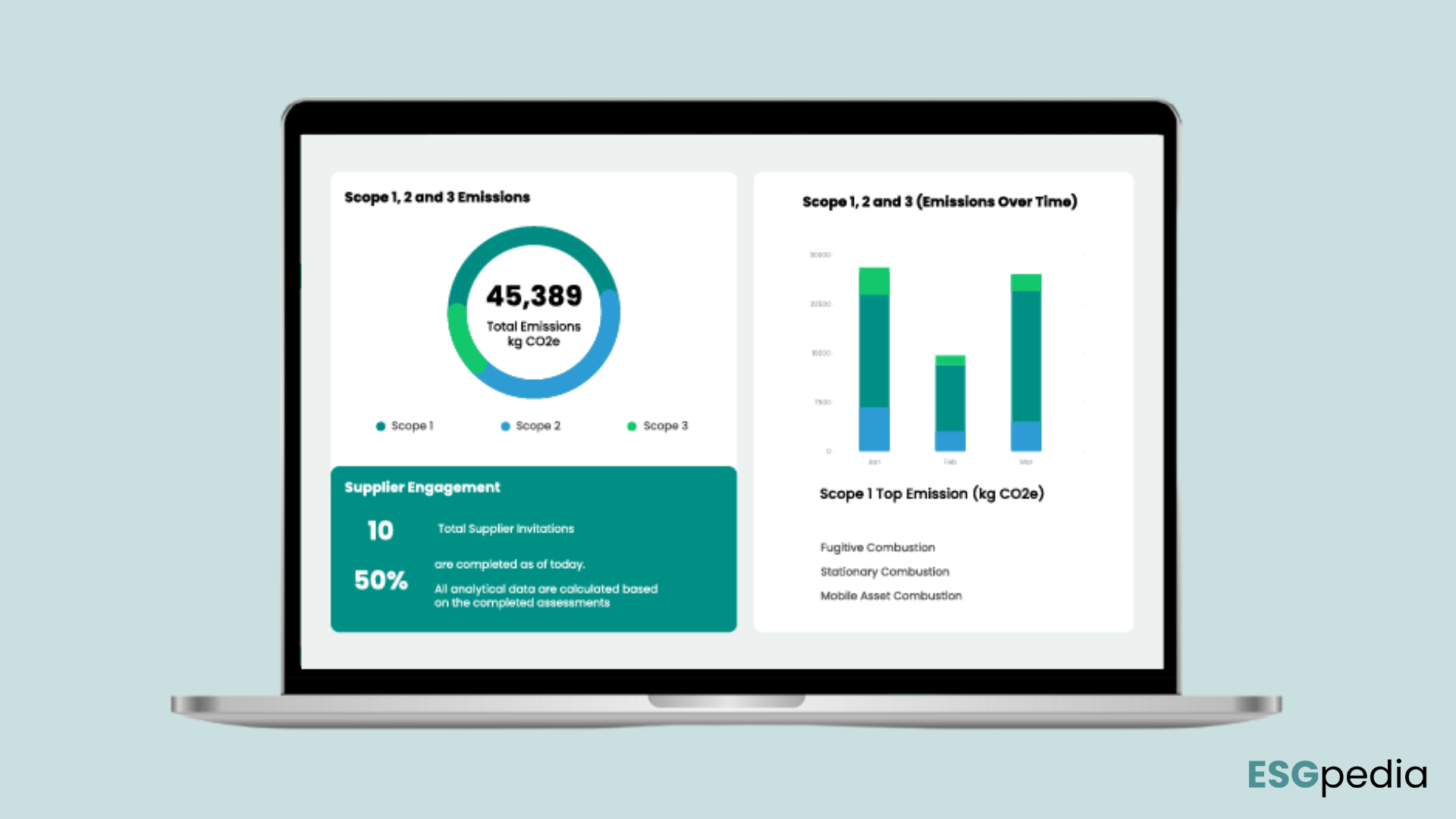
To streamline the carbon calculation process and ensure accuracy, companies can leverage tools like the ESGpedia Carbon Calculator. Built for credibility and accuracy, and validated under the ISO14064 methodology, ESGpedia enables the calculation of GHG emissions, utilising its extensive base of more than 280,000 emission factors hyper-localised to all APAC countries, covering over 1,100 product categories. It helps companies gather accurate data, apply appropriate emission factors to ensure the highest level of accuracy, and generate detailed GHG emissions reports.
For comprehensive reporting, large corporates should also assess and calculate their Scope 3 emissions, which include all other indirect emissions that occur in the value chain of the company. While more complex to calculate, understanding and reporting on Scope 3 emissions provides a complete view of a company’s carbon footprint, allowing for a comprehensive decarbonisation strategy. The ESGpedia Carbon Calculator maps every part of the value chain and product life cycle, supporting various Scope 3 calculation methods, including transaction-based and life cycle approach. To find out more about Scope 3 emissions, click here.
Step 3: Set Clear and Achievable Goals
Setting clear and achievable sustainability goals is essential for translating sustainability aspirations into tangible outcomes. The SMART criteria — Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound — provides a practical framework for this process.
- Specific – Goals should be precise and well-defined. For instance, aiming to reduce carbon emissions from employees commuting by 50% provides a clear target.
- Measurable – To track progress, goals must be quantifiable. Employee commuting surveys can be used to measure reductions in emissions.
- Achievable – Goals should be realistic. Encouraging employees to cycle, use public transport, or car-pool can make commuting emission reductions attainable.
- Relevant – Goals must align with broader sustainability objectives. Reducing commuting emissions is relevant as it addresses significant Scope 3 emissions.
- Time-Bound – Setting a deadline, such as achieving a 50% reduction by 2030, creates urgency and maintains momentum.
Examples of common sustainability goals include reducing overall emissions, improving energy efficiency, reducing water usage, and enhancing supply chain sustainability. To implement these goals, develop a Strategic Action Plan that defines actions, assigns responsibilities, and sets timelines. This structured approach ensures accountability and progress. A good reference is the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), which can provide guidance for setting emissions reduction targets in line with climate science. Additionally, leveraging digital ESG solutions like ESGpedia can aid in setting and measuring these goals.
Step 4: Engage and Educate Stakeholders
Engaging and educating stakeholders, including employees and suppliers, is crucial for successful sustainability initiatives. A collective commitment to sustainability goals enhances implementation and maximizes benefits.
From top management to frontline employees, everyone must understand and support the sustainability vision to drive meaningful change. Suppliers, especially with the rising scrutiny of Scope 3 emissions, should also be engaged. ESGpedia’s Supplier Engagement Module aims to help large corporates manage and streamline engagement of their ecosystem of suppliers, from data collection to monitoring and getting them to take action towards decarbonisation, to align suppliers with the organisation’s sustainability goals.
Strategies for Effective Communication
Effective communication is key to educating stakeholders about your sustainability vision and goals. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Annual Sustainability Reports: Publishing an annual sustainability report is a primary method for communicating your progress, which includes a comprehensive overview of your sustainability efforts, achievements, and areas for improvement.
- Dedicated Website or Webpage: Create a section on your company’s website for sustainability-related information, goals, progress updates, and resources.
- Honest and Transparent Communication: Share both successes and challenges to build trust and credibility, as exemplified by companies like Patagonia.
- Training Programs: Offer workshops, webinars, or e-learning modules on topics like waste reduction, energy efficiency, and sustainable procurement to equip stakeholders with necessary knowledge and skills.
Step 5: Monitor, Report, & Improve
Continuous monitoring and reporting are essential for ensuring that sustainability goals are met and for driving ongoing improvements.
Gaining executive commitment is a vital step in this process. Appointing an internal sustainability champion to lead the efforts and developing a robust employee engagement model can significantly enhance the success of sustainability initiatives. According to the 2012 Report of Sustainability Leaders by VOX Global and Net Impact Berkeley, 78% of respondents identified top management as key contributors to embracing sustainability, while 81% pointed to their colleagues across the company as primary drivers of success.
To effectively monitor and report on sustainability efforts, companies also need to set up systems to track progress on various metrics. Regularly reviewing the collected data allows companies to adapt and improve their action plans.
For SMEs
For resource-strapped SMEs, the approach can be simplified. SMEs can establish clear systems and processes for tracking their sustainability goals, ensuring that these processes are integrated into their daily operations. While executive commitment is important, the success of sustainability initiatives in SMEs often relies on the collective effort of all employees.
For further improvement, SMEs should connect to the ESGpedia marketplace, which offers sustainable finance options and simple decarbonisation solutions. This access is tailored to the needs of businesses of every size, helping them enhance their sustainability practices effectively.
Reporting to meet Global Reporting Standards and Local Regulations
To achieve compliance, businesses, regardless of size, should report in accordance with international or local frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), Simplified ESG Disclosure Guide (SEDG) for Malaysian SMEs, and Sustainability Report Form (SuRe Form) for Filipino businesses, amongst others. Adhering to global standards and local regulations offers several benefits, including credibility, competitiveness, benchmarking, and regulatory compliance. To find out more about common international and country-specific sustainability reporting standards in place, click here.
Decarbonise and seek ESG solutions on the ESGpedia Marketplace
On the ESGpedia Marketplace, businesses can:
- Seek Sustainable Financing: Collaborate with our ecosystem of banks.
- Verify Sustainability Reports: Use our third-party ESG assurance partners like Bureau Veritas.
- Outsource Expertise: Engage ESG consultants for specialized knowledge.
- Offset emissions through Carbon Offsets or Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs): Motivate consumers to purchase carbon offsets to mitigate the environmental impact of their purchases.
Contact us to learn more about the wide variety of ESG solutions available on ESGpedia.
Common Obstacles and Solutions

Manual Data Collection
Often, data collection is a vast exercise requiring multiple teams and stakeholders. It also usually happens sporadically, typically during specific reporting periods like the annual reporting season, which means organisations might not have a complete picture of their sustainability performance year-round. This is especially difficult for SMEs, who are unable to dole out the labour for such tasks.
To combat this, companies need to establish consistent and timely data collection protocols across the organisation. This is where digital ESG data and technology platforms like ESGpedia can come in as a centralised database to help streamline the data collection, management, and reporting process.
Budget Constraints
Budget constraints can hinder the implementation of comprehensive sustainability initiatives. Business can instead focus on certain low-cost, high-impact initiatives such as energy efficiency upgrades, waste reduction programs, and employee engagement campaigns. They can also leverage financial incentives such as green loans, grants, and tax credits. To find out more about sustainable finance, click here.
Lack of Resources
Many organisations struggle with limited resources, making it difficult to prioritize actions and seek external support. Firstly, companies need to focus on the most impactful and achievable sustainability initiatives. Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to identify actions that provide the greatest return on investment. Moreover, businesses, especially SMEs, need to leverage external resources and expertise. To find out about local and international resources, click here.
Pathway to Sustainable Success
Creating a corporate sustainability action plan involves a structured approach to ensure meaningful and lasting impact. The five essential steps include assessing your current sustainability status, accurately measuring emissions, setting clear and achievable SMART goals, engaging and educating stakeholders, and continuously monitoring, reporting, and improving your strategies.
By embedding sustainability into your company’s DNA, you contribute to a healthier planet while strengthening your business’s resilience and long-term success. For a comprehensive approach to achieving your corporate sustainability goals, explore ESGpedia, available in various pricing tiers to match your business ESG needs. It offers a range of features and solutions, including carbon calculation, sustainability reporting, supplier engagement module, dashboard and analytics, and a marketplace of extensive partners across Asia, to support businesses of all sizes in their sustainability journey. Embrace these steps and leverage the right digital tools and ESG solutions to pave the way for a sustainable future for your organisation.